In the process of software development, the adoption of methodologies that prioritize flexibility, collaboration, and adaptability is imperative. Agile methodology has emerged as a cornerstone in modern software development, revolutionizing traditional approaches and providing a framework that fosters responsiveness to change.
What is Agile Methodology
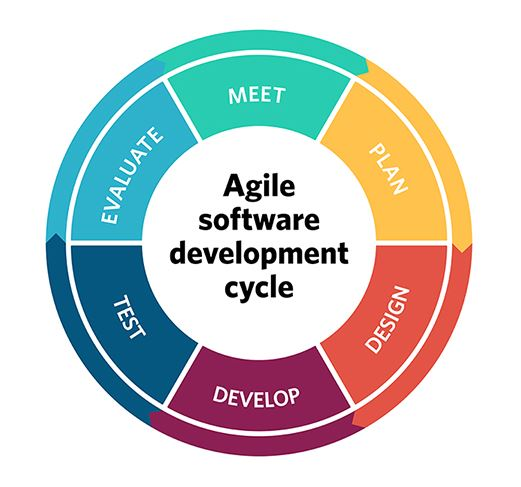
Agile methodology is an iterative and incremental approach to software development that emphasizes adaptability, collaboration, and customer satisfaction.
Originating from the Agile Manifesto, a set of guiding values and principles for agile software development, Agile methodology seeks to replace rigid, linear development processes with a more flexible and iterative model.
Key Principles of Agile Methodology

Individuals and Interactions over Processes and Tools
Agile places a strong emphasis on the value of people and their interactions. Effective communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders are prioritized over rigid processes and tools.
Working Software over Comprehensive Documentation
While documentation is essential, Agile values a functional end product. It encourages developers to focus on delivering a working software product rather than becoming overly fixated on exhaustive documentation.
Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation
Agile emphasizes continuous collaboration with customers and stakeholders throughout the development process. This ensures that the end product aligns with customer expectations and can adapt to evolving needs.
Responding to Change over Following a Plan
Agile embraces change as a natural and expected part of the development process. Teams are encouraged to respond to changing requirements and priorities, adapting their plans and strategies accordingly.
Key Practices of Agile Methodology
Scrum Framework
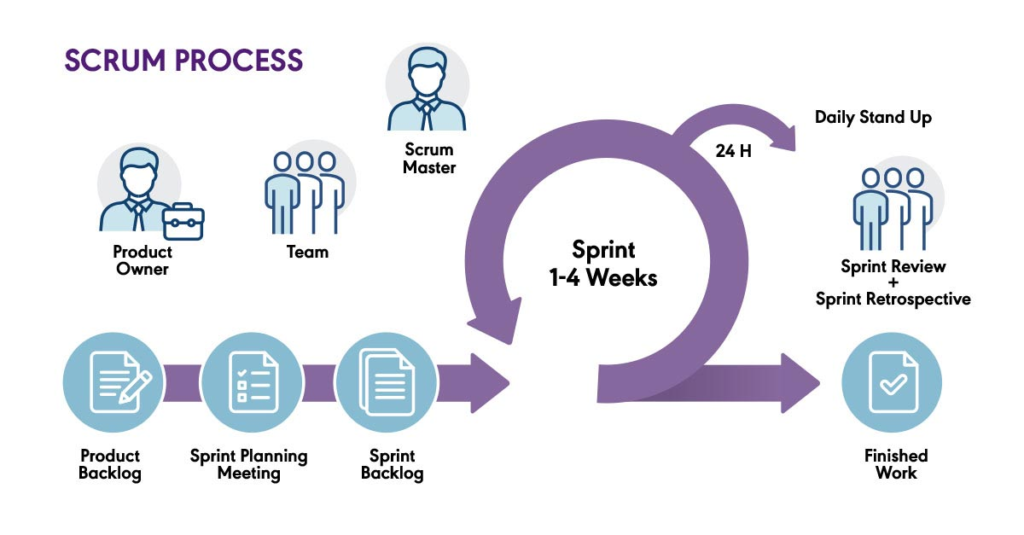
Scrum is one of the most widely adopted frameworks within Agile methodology. It divides the development process into fixed-length iterations called sprints, typically two to four weeks long.
The Scrum framework includes key roles such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, promoting collaboration and delivering incremental value at the end of each sprint.
Kanban Method
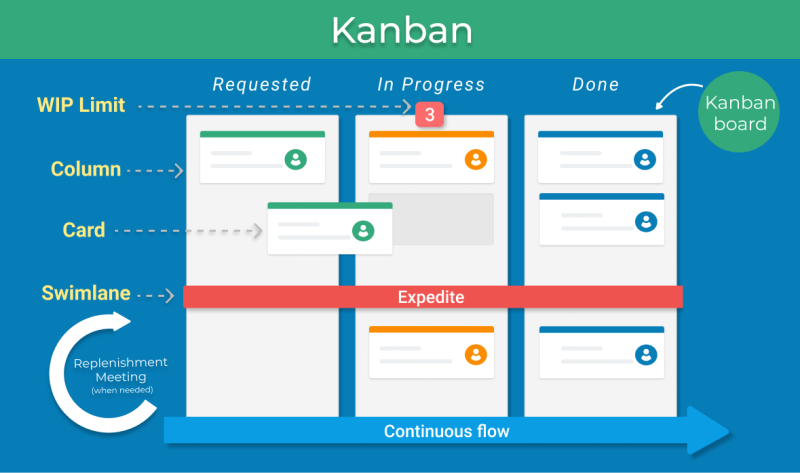
Kanban is a visual management method that helps teams manage workflow efficiently. It uses a visual board to represent work items, allowing teams to monitor progress and optimize their processes continuously. Kanban promotes a pull-based system, where work is pulled only when there is capacity.
Extreme Programming (XP)
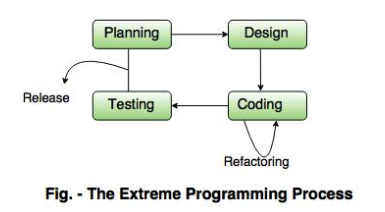
XP is an Agile methodology that focuses on improving software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. It incorporates practices such as pair programming, continuous integration, test-driven development (TDD), and frequent releases to ensure high-quality, adaptable software.
Transformative Impact of Agile on Software Development
Increased Flexibility and Adaptability
Agile’s iterative approach allows for continuous feedback and adjustment, enabling teams to respond promptly to changing requirements. This increased flexibility is particularly crucial in industries where rapid innovation and changing market conditions are the norm.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Agile methodologies prioritize communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders. Regular meetings, such as daily stand-ups and sprint reviews, foster a culture of open communication, leading to improved team dynamics and a shared understanding of project goals.
Customer-Centric Development
By involving customers throughout the development process, Agile ensures that the end product meets customer expectations. Continuous feedback loops allow for adjustments based on customer input, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and a product that better aligns with market needs.
Early and Predictable Delivery
Agile’s focus on incremental development and regular releases enables teams to deliver a minimum viable product (MVP) quickly. This approach provides stakeholders with tangible results early in the development cycle and allows for predictability in terms of feature delivery.
Improved Product Quality
Agile practices, such as test-driven development and continuous integration, contribute to enhanced product quality. By incorporating testing at every stage of development, teams can identify and address issues early, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product.
Challenges and Considerations
While Agile methodologies offer numerous benefits, their adoption is not without challenges. Some common considerations include:
- Cultural Shift
Implementing Agile often requires a cultural shift within organizations. Teams accustomed to traditional, waterfall-style development may initially find it challenging to adapt to the iterative and collaborative nature of Agile.
- Resource Allocation
Agile requires dedicated and cross-functional teams. Organizations must allocate resources appropriately to ensure teams have the skills and capacity needed to deliver high-quality results within short development cycles.
- Client Involvement
Agile relies on continuous client involvement. This may pose challenges if clients are unable to commit the necessary time and resources to participate actively in the development process.
Conclusion
In the fast-paced world of modern software development, Agile methodology has proven to be a transformative force.
By prioritizing flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction, Agile frameworks empower development teams to navigate the complexities of evolving requirements and dynamic market conditions successfully. While challenges exist, the benefits of increased adaptability, improved collaboration, and customer-centric development position Agile as an essential approach for organizations seeking to thrive in the ever-changing landscape of software development.
As technology continues to advance, the principles and practices of Agile methodology remain integral to achieving success in the delivery of innovative and high-quality software solutions.



